Heart attack, angioplasty and bypass surgery have become very common today. Cardiovascular disease is the number one cause of death across the world, and India is now considered the world capital of heart disease.
While several treatment options exist, they can be risky, painful and expensive. More importantly, the results don’t always match expectations. This is why it makes more sense to focus on prevention before it’s too late.
You can check your risk of heart disease early and take steps to protect yourself. Understanding what increases your risk of heart disease helps you take the right action at the right time.
There are many factors that influence your chances of developing cardiovascular disease. Some cannot be changed, such as increasing age. These are called non-modifiable risk factors.
On the other hand, several factors can be improved through lifestyle changes and proper medication. These are known as modifiable risk factors, and working on them can greatly lower your overall risk.
Non-Modifiable risk factors
Age: Aging increases the risk of heart disease but now a days many younger people are also getting heart attacks
Gender: Males are more prone to heart diseases compared to females until menopause, after menopause females are also at same risk as males.
Family history: If your parents or siblings have heart disease then it increases your risk also for heart disease
Modifiable risk factors
Diabetes: Diabetes has multiple complications including heart disease. If you have diabetes then try to keep it well controlled.
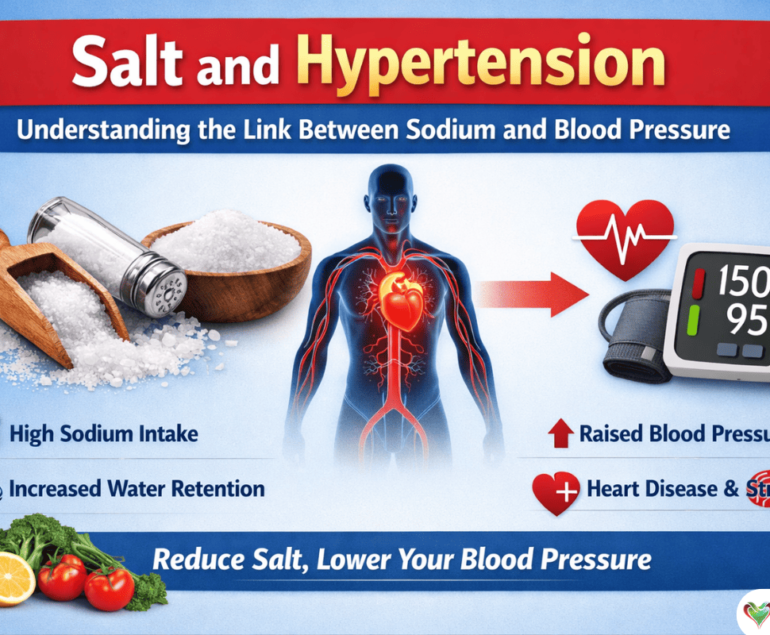
Hypertension: High blood pressure also is one of the major risk factors for heart disease and one must keep it under controlled.
Dyslipidemia: High level of LDL cholesterol and triglycerides increases the risk of developing blockage in arteries including the arteries of heart.
LDL: Increased low-density lipoprotein (LDL) also known as bad cholesterol, can build-up fatty acid deposit in arteries causing the blockages. One should keep the level of LDL cholesterol less than 100 mg/dl
HDL: High-density lipoprotein (HDL) also known as good cholesterol.
HDL levels less than 40 mg/dl is also associated with increased risk for heart disease.
Triglycerides: Triglycerides are fats from the food we eat that are carried in the blood. High triglycerides combined with high cholesterol raise your risk of heart attack, strokes and pancreatitis. Keep your Triglyceride levels under 150 mg/dl
High sensitivity C – Reactive Protein (hsCRP): Even minor elevation in hsCRP level have shown to be associated with increased cardiovascular risk
Low risk: hsCRP less than 1mg/L
Best way to lower CRP is through exercise, weight loss and dietary control.
Obesity: Being overweight or having central obesity (big tummy) could also lead to heart disease
Keep your BMI (body mass index) between 18.5 to 24.9 kg/m2 and According to the World Health Organization (WHO), a moderate WHR is: 0.9 or less in men and 0.85 or less for women
Smoking: Smoking and tobacco are major risk factors for Cardio vascular disease as tobacco causes hardening of blood vessels. Quit smoking and all types of tobacco consumptions.
Sedentary Lifestyle: Living an inactive life also could lead to the heart disease. Try to live an active life. Start walking daily for at least 30 to 45 minutes.
Mental stress: In today’s fast life, stress has become the way of life and mental stress is a major cause of heart disease particularly in young generation. Try to manage your stress, practice yoga and meditation, cultivate few hobbies and spend some quality time with family and friends
Unhealthy diet: Fast life and fast food has become the culture for this generation leading to explosion of the heart disease. Avoid food with too much fat, sugar or refined flour. Eat lots of vegetables and fruits as they are rich in fibers, anti-oxidants and micro nutrients.