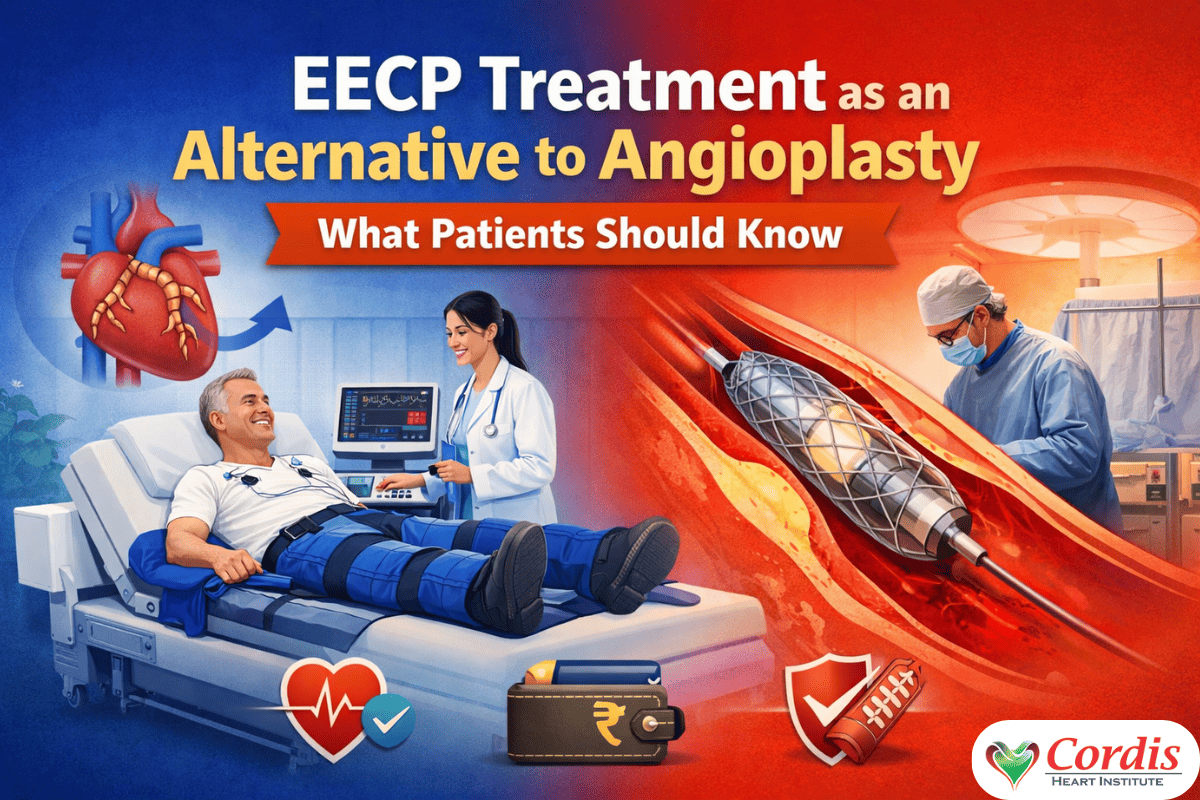
Heart blockage is a common reason people see a cardiologist. Traditionally, angioplasty and stenting have been the primary treatment options for these types of patients. Angioplasty can save lives; however, not all patients can tolerate the stress of an in-hospital surgical procedure or the experience of being hospitalized and recovering from that procedure. That’s why EECP Treatment was developed as an alternative to both Angioplasty and Stenting.
Currently, many individuals who have heart blockages are looking for treatment options not requiring surgical intervention. In this article you will find out what EECP is, how it compares to both Angioplasty and Stenting, who it’s intended for and what physicians recommend.
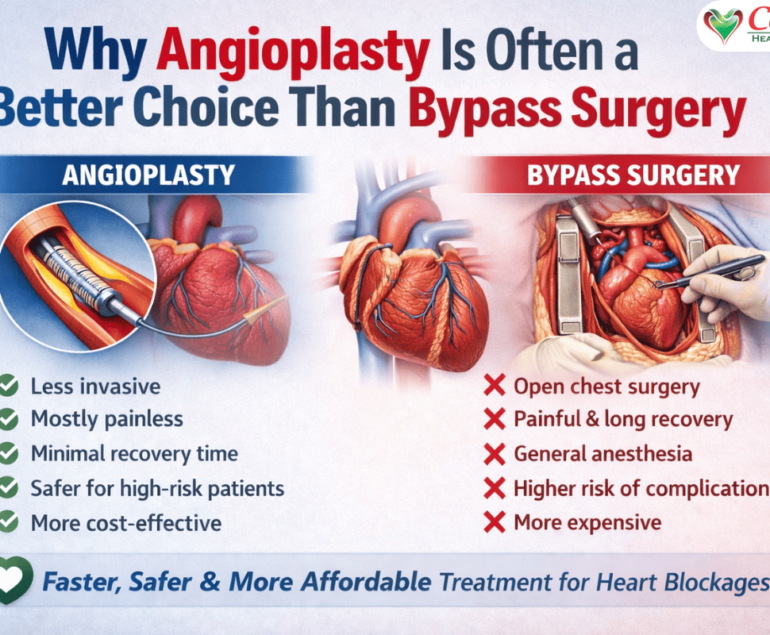
Understanding Angioplasty and Why Patients Look for Alternatives
Angioplasty is a medical procedure used to open narrowed or blocked coronary arteries. A thin tube with a balloon is guided into the heart’s blood vessels. Once inflated, it pushes plaque aside, and in most cases, a stent is placed to keep the artery open.
Doctors often recommend angioplasty when:
- Chest pain becomes frequent
- Blood flow to the heart is severely reduced
- Medications alone are not helping
That said, many patients hesitate due to real concerns:
- It is an invasive procedure
- There is a risk of re-blockage or stent complications
- Recovery may involve lifestyle limits and long-term medication
These concerns push patients to search for a non-surgical heart treatment that still delivers relief.
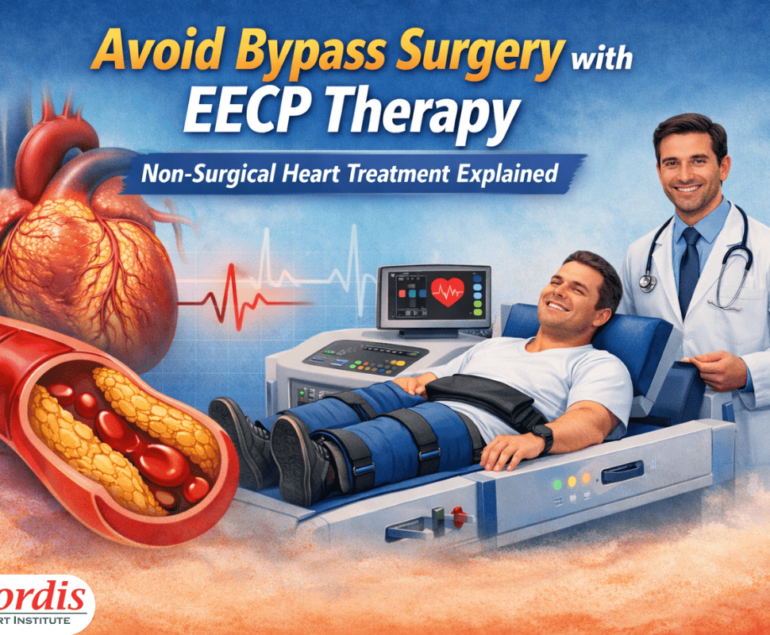
What Is EECP Treatment? A Non-Surgical Heart Therapy
EECP stands for Enhanced External Counterpulsation. It is a non-invasive therapy designed to improve blood flow to the heart without surgery, stents, or anesthesia.
How EECP Works
- The patient lies comfortably on a bed
- Pneumatic cuffs are wrapped around the legs
- These cuffs inflate and deflate in sync with the heartbeat
- This action pushes oxygen-rich blood toward the heart
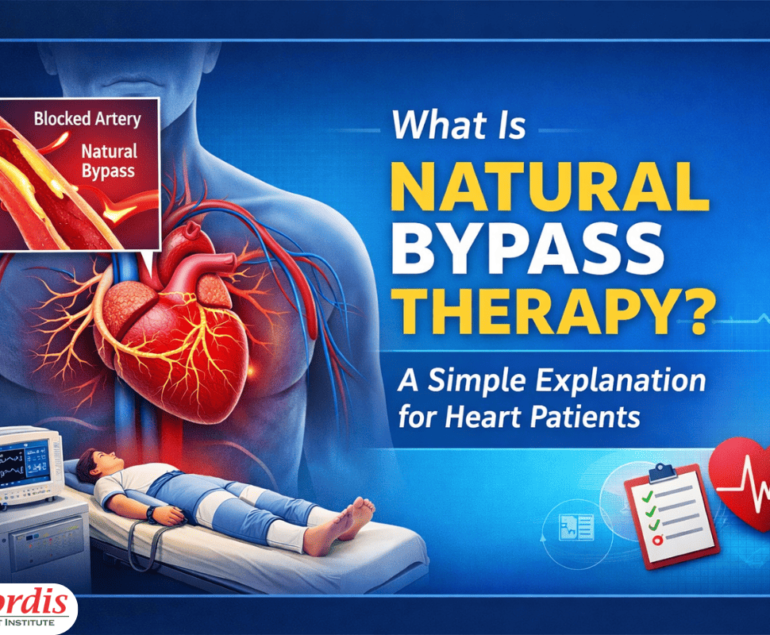
Over time, EECP helps the body develop natural bypass channels called collateral circulation.
Treatment Structure
- Outpatient therapy
- Usually 35 sessions
- Each session lasts about one hour
- No hospital admission required
Patients often resume normal activities right after each session.
EECP vs Angioplasty: Key Differences Patients Should Know
|
Factor |
EECP Treatment |
Angioplasty |
|
Procedure type |
Non-invasive |
Invasive |
|
Hospital stay |
Not required |
Often required |
|
Anesthesia |
Not needed |
Needed |
|
Recovery time |
Immediate |
Days to weeks |
|
Risk level |
Low |
Moderate |
|
Long-term relief |
Symptom-focused |
Structural correction |
EECP vs angioplasty is not about which is “better” but about which suits a patient’s condition, age, and risk profile.
How EECP Treatment Helps Heart Patients Without Surgery
EECP therapy benefits go beyond symptom control. It helps the heart work smarter, not harder.
Key benefits include:
- Better blood flow to blocked areas
- Reduced chest pain and shortness of breath
- Improved stamina for daily activities
- Fewer hospital visits for heart symptoms
Many patients report improved walking distance, better sleep, and more confidence in daily life.
Who Can Consider EECP as an Alternative to Angioplasty?
EECP treatment for heart disease is commonly considered for:
- Patients advised angioplasty but seeking non-surgical options
- Elderly patients with surgical risks
- Patients with recurring chest pain after angioplasty
- Those not suitable for bypass or stenting
When EECP May Not Be Suitable
- Severe valve disease
- Certain rhythm disorders
- Active blood clots
A cardiologist’s evaluation is always necessary before starting therapy.
Safety, Risks, and Side Effects of EECP Treatment
EECP has a strong safety record when done under medical supervision.
Common Mild Side Effects
- Temporary leg discomfort
- Skin redness under cuffs
- Mild muscle fatigue
Serious complications are rare. Proper screening helps avoid risks, making EECP one of the safest non-invasive heart therapies available today.
EECP Treatment Cost Compared to Angioplasty
In India, EECP treatment cost is generally lower than angioplasty.
- EECP: Often ranges from ₹1.2 to ₹1.35 lakhs for a full course
- Angioplasty: Can range from ₹2.5 to ₹6+ lakhs depending on stents and hospital
When long-term medication and repeat procedures are considered, EECP can be a cost-friendly alternative for suitable patients.
What Do Doctors Say About EECP as an Angioplasty Alternative?
Cardiologists worldwide accept EECP for patients with chronic stable angina, especially when surgery carries higher risk.
Doctors emphasize:
- EECP does not replace angioplasty in emergencies
- It works best when combined with medication and lifestyle care
- Patient selection is key to success
A heart specialist’s guidance remains the most important step in decision-making.
FAQs: EECP Treatment as an Alternative to Angioplasty
Can EECP treatment avoid angioplasty?
In some patients, yes. It can reduce symptoms enough to delay or avoid surgery.
Is EECP treatment permanent?
Results often last years, especially with lifestyle changes.
How long do EECP results last?
Many patients see benefits for 2–5 years or more.
Is EECP painful?
No. Most patients describe it as firm pressure, not pain.
Can EECP be done after angioplasty?
Yes. It is often used for symptom relief after stenting.
How soon can patients see improvement?
Some notice changes within 10–15 sessions.
Final Thoughts: Choosing the Right Heart Treatment
EECP Treatment as an Alternative to Angioplasty offers hope to patients who want relief without surgery. While angioplasty remains essential for many cases, EECP fills an important gap for those seeking a safer, non-invasive path.
The right choice depends on heart condition, risk factors, and medical advice. There is no one-size-fits-all answer, only informed decisions.
If you or a loved one is exploring non-surgical heart treatment options:
Early action can improve comfort, confidence, and daily life.