Heart disease is one of the most common health problems today. When blood flow to the heart muscle is reduced due to blocked or narrowed arteries, doctors usually recommend a procedure to restore proper circulation. Two common treatment options are angioplasty and bypass surgery.
In many cases, angioplasty is preferred over bypass surgery because it is less invasive, causes less pain, and allows faster recovery. This blog explains angioplasty in simple terms, compares it with bypass surgery, and helps patients understand why angioplasty is often chosen as the first line of treatment.
What Is Angioplasty?
Angioplasty, also known as balloon angioplasty with stent placement, is a non-surgical procedure used to open blocked or narrowed coronary arteries.
During angioplasty:
- A thin catheter tube is inserted through an artery in the wrist or leg
- The catheter is guided to the blocked heart artery
- A small balloon is inflated to widen the artery
- A stent is placed to keep the artery open
- The catheter is removed after the procedure
The procedure is done under local anesthesia, and the patient remains conscious throughout.
What Is Bypass Surgery?
Bypass surgery, also called coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), is a major open-heart operation.
In bypass surgery:
- The chest is cut open
- The heart is accessed under general anesthesia
- A healthy blood vessel from the leg, arm, or chest is used
- This vessel creates a new route for blood flow around the blocked artery
It is a complex procedure that requires intensive care and long recovery.
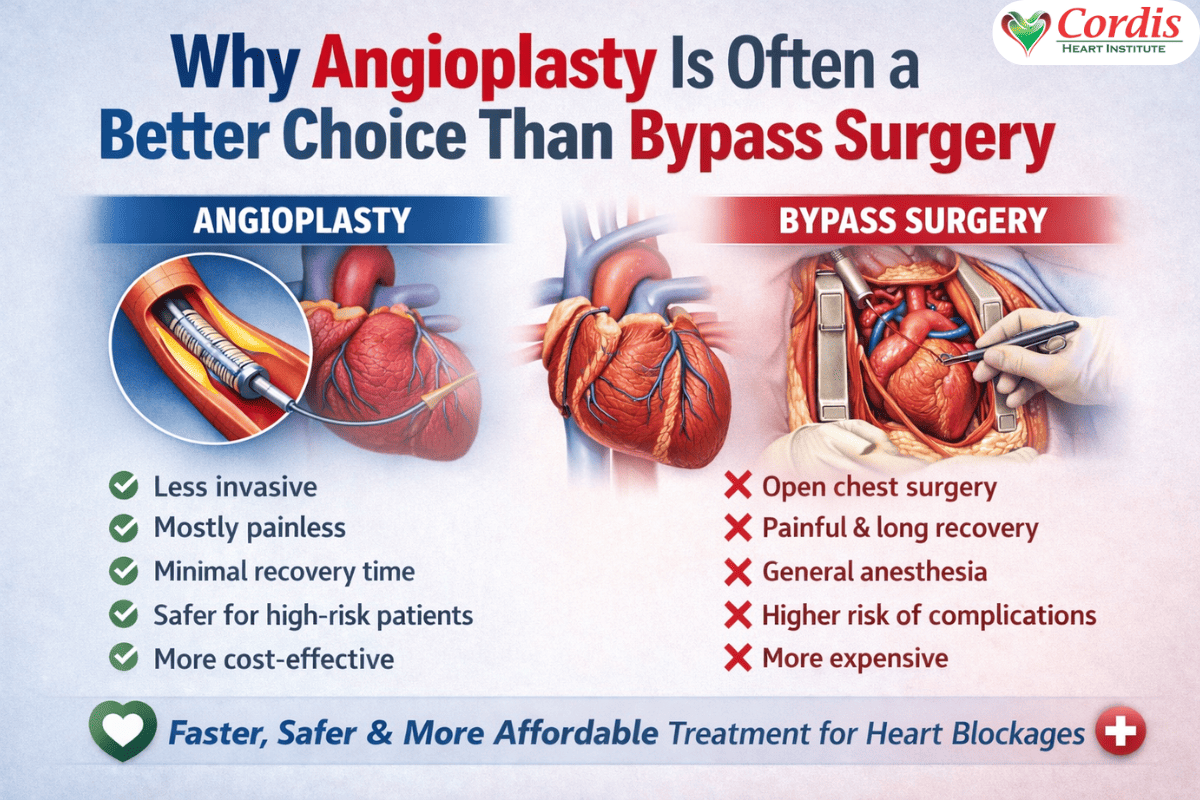
Angioplasty vs Bypass Surgery: A Clear Comparison
1. Level of Invasiveness
Angioplasty is a minimally invasive procedure. There is no chest opening and no major surgical wound.
Bypass surgery involves cutting open the chest and handling the heart directly.
2. Pain and Discomfort
Angioplasty is mostly painless. Patients may feel mild discomfort at the catheter insertion site.
Bypass surgery causes significant pain after surgery due to chest incision and muscle healing.
3. Hospital Stay
Angioplasty usually requires a hospital stay of 1 to 2 days.
Bypass surgery often needs 7 to 10 days of hospitalization, sometimes longer.
4. Recovery Time
Most angioplasty patients return to daily activities within a week.
Bypass surgery recovery can take 8 to 12 weeks, with strict physical limitations.
5. Cost
Angioplasty is more cost effective compared to bypass surgery.
Bypass surgery is expensive due to operation costs, ICU care, and long hospital stay.
6. Blood Loss
Angioplasty involves minimal blood loss and rarely requires transfusion.
Bypass surgery has higher blood loss and often needs blood transfusion.
Why Angioplasty Is Often the Better Choice
Faster Recovery and Return to Normal Life
One of the biggest advantages of angioplasty is quick recovery. Patients can walk within hours and resume work within a few days. This is especially helpful for working individuals and elderly patients.
Lower Risk of Complications
Since angioplasty does not involve open surgery, the risk of infection, stroke, and other surgical complications is lower. Bypass surgery carries higher risk due to anesthesia and prolonged operation time.
Safer for High-Risk Patients
Patients with diabetes, advanced age, or other medical conditions may not be ideal candidates for major surgery. Angioplasty is often safer for such patients.
No General Anesthesia
Angioplasty is done under local anesthesia, which reduces anesthesia-related risks. Bypass surgery requires general anesthesia, which can be risky for some patients.
When Is Bypass Surgery Still Needed?
Although angioplasty has many advantages, bypass surgery may still be recommended in some situations, such as:
- Multiple severe blockages
- Left main coronary artery disease
- Diffuse long blockages not suitable for stents
- Failed angioplasty or repeated stent blockages
The final decision depends on angiography findings and the patient’s overall health.
Long-Term Results of Angioplasty
Modern stents, especially drug-eluting stents, have improved long-term outcomes. When combined with lifestyle changes and proper medication, angioplasty offers good results for many patients.
To maintain benefits after angioplasty:
- Quit smoking
- Control blood pressure and diabetes
- Follow a heart-friendly diet
- Take prescribed medicines regularly
- Stay physically active as advised
Common Myths About Angioplasty
Myth: Angioplasty is temporary
Fact: With proper care, angioplasty can provide long-term relief
Myth: Bypass is always better
Fact: Angioplasty is often the first choice for suitable blockages
Myth: Angioplasty is risky
Fact: It is a widely used and safe procedure when done by experienced cardiologists
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is angioplasty better than bypass surgery for everyone?
No. Angioplasty works best for single or limited blockages that can be treated with stents. Bypass surgery may be advised for multiple severe blockages, left main artery disease, or when stents are not suitable. The right option depends on angiography results and overall health.
Is angioplasty painful?
Angioplasty is mostly painless. It is done under local anesthesia, so patients stay awake. Some people feel mild pressure at the catheter site, which settles quickly.
How long does an angioplasty procedure take?
In most cases, angioplasty takes 30 minutes to 1 hour. Complex cases may take longer, but it is still much shorter than bypass surgery.
How soon can I walk after angioplasty?
Most patients can sit up and walk within a few hours. Doctors usually allow light movement the same day or the next morning.
When can I return to work after angioplasty?
Many patients return to normal work within 5 to 7 days, depending on their job type and doctor’s advice.
Is angioplasty safe for elderly patients?
Yes. Angioplasty is often safer for elderly patients because it avoids major surgery, general anesthesia, and long recovery time.
Does angioplasty completely cure heart blockage?
Angioplasty opens blocked arteries and improves blood flow, but it does not remove the cause of heart disease. Long-term success depends on lifestyle changes and regular medication.
Can blockages come back after angioplasty?
There is a small chance of re-narrowing, especially if medicines are not taken properly. Modern drug-coated stents have reduced this risk significantly.
Is bypass surgery more permanent than angioplasty?
Bypass surgery may last longer in some complex cases, but angioplasty also provides long-term relief for many patients when combined with proper care and follow-ups.
What lifestyle changes are needed after angioplasty?
Patients should stop smoking, control blood pressure and diabetes, eat a heart-friendly diet, stay active as advised, and take medicines regularly.
Is angioplasty expensive?
Angioplasty is generally more affordable than bypass surgery due to shorter hospital stay, fewer complications, and faster recovery.
How do doctors decide between angioplasty and bypass surgery?
Doctors consider factors like number of blockages, location, severity, heart function, age, and other medical conditions before suggesting the best treatment.
Final Thoughts
Angioplasty has changed the way heart blockages are treated. It is less painful, more affordable, and allows patients to recover faster compared to bypass surgery. While bypass surgery still has its place in advanced cases, angioplasty is often the better and safer option for many patients.
If you or a loved one has been advised heart treatment, discussing angioplasty as an option with your cardiologist can help you make an informed decision based on your condition and lifestyle.